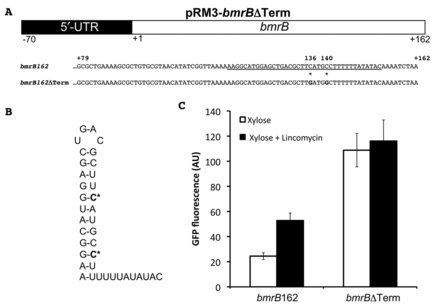
The terminator in bmrB is required for lincomycin-induced bmrCD transcription. A. Schematic representation of a part of plasmid pRM3-bmrBΔTerm. Nucleotides 79–162 of the intact bmrB gene and its bmrBΔTerm derivative are shown; C to G point mutations at positions 136 and 140 are marked with an asterisk (*). The predicted terminator sequence is underscored. B. Predicted structure of the terminator sequence with the position of the C to G point mutations marked in bold and with an asterisk (*). C. Maximum GFP expression levels measured for B. subtilis strains carrying pRM3-bmrB162 (marked bmrB162) or pRM3-bmrBΔTerm (marked bmrBΔTerm) upon induction with xylose (white bars) or xylose and 0.75 μg/ml lincomcyin (black bars).






